Williamson Ether Synthesis Mechanism
If the halides are sterically demanding and there are accessible protons in the β-position the alkoxide will act as a base and side products derived from elimination are isolated instead. Ethers are compounds with one oxygen that is attached with two R groups.

Complete Collection Organic Chemistry Chemistry Notes Organic Chemistry Study
In this work we deploy a three-faceted approach that combines experimental probing detailed kinetic modelling and quantum-mechanical calculations for the study of the mechanism and regioselectivity of a Williamson ether synthesis which is of interest because of its simplicity and its broad scope in laboratory and industrial synthesis.

Williamson ether synthesis mechanism. This reaction helped to prove the structure of ethers. Mechanism of the Williamson Synthesis. This mechanism which was also used in lab ten is a two-step process. The alkoxide ion is prepared by the reaction of an alcohol with a strong base such as sodium hydride. Williamson synthesis generally involves nucleophilic displacement of a halide ion or a good leaving group by an alkoxide ion. The Williamson ether synthesis follows the following mechanism- Prev Question Next Question 0 votes.
So if you react an alcohol with a strong base something like sodium hydride we know that the hydride portion of the molecule is going to function as a strong base. The Williamson Ether Synthesis A. Unlike the formation of alkoxides which require a strong base such as sodium hydride phenoxides are easily produced using hydroxide ion. The mechanism begins with the base abstracting the proton from the alcohol to form an alkoxide intermediate. Asked Jun 21 2019 in Chemistry by ShreenikaRaj 904k points The Williamson ether synthesis follows the following mechanism-A. Williamson ether synthesis mechanism and example Synthesis of phenacetin common ochem lab reaction.
An SN1 mechanism is a two-step mechanism and racemization occurs. The Williamson ether synthesis is a reaction that converts alcohols R-OH into ethers R-O-R. Williamson Ether Synthesis. It contains plenty of examples a. Williamson ether synthesis The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction used to convert an alcohol and an alkyl halide to an ether using a base such as NaOH. The first use of the Williamson ether synthesis was seen mainly used for precursors such as alcohol and alkyl halide.
This reaction was developed by Alexander Williamson in 18502 Typically it involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide via an SN2 reaction. The Williamson Ether Synthesis can specifically be found in sections 17-2 and 18-2. 11 in the 9th edition McMurry textbook. Only works with 0 1 alkyl halides since 2 and 3 alkyl halides will favor E2. Nucleophile attacks strong nucleophile from backside of leaving group product has inverted stereochemistry. In this mechanism alkoxde ion attacks on carbon atom of alkyl halides by following SN² mechanism to form ether.
Introduction It would be beneficial if you review the chapter on substitution reactions in your textbook prior to lab. The name given for the SN2 substitution of an oxide with an alkyl halide. The Williamson Ether Synthesis We have seen many times when discussing the S N 2 mechanism that ethers are common products of nucleophilic substitution reactions. Action of alcoholic sodium alkoxide on alkyl halides to form ethers is known as Williamsons synthesis. Mechanism- This reaction is given by primary alkyl halidesTertiary alkyl halides preffer to undergo elimination. They are synthesized by reacting alkyl halides or other substrates with good leaving groups with alkoxides.
Sign in to download full-size image. The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction forming an ether from an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol alkoxide. We know that alcohols can function as weak acids. So lets look at the mechanism for the Williamson ether synthesis where you start with your alcohol. To produce molecules that can have a variety of uses ethers should be used. First the alcohol is deprotonated using a strong base to create an alkoxide anion.
The nucleophilic substitution of halides with alkoxides leads to the desired products. The first step in this reaction is forming the conjugate base of the alcohol called an alcoxide by reacting the alcohol with sodium metal. Experiment 12 The Williamson Ether Synthesis pg. Aryl methyl ethers can be obtained using dimethyl sulfate. A Williamson Ether synthesis is carried out using an alcohol and an alkyl halide. The phenoxide ion then acts as a nucleophile and displaces a halide ion from an alkyl halide.
The reaction takes place as an S N 2 reaction of a primary alkyl halide with an alkoxide ion. Index Mechanism of Williamson Reaction Conditions Required for the Reaction. It occurs by an SN 2 reaction in which a metal alkoxide displaces a halide ion from an alkyl halide. This reaction is important in the history of organic chemistry because it helped prove. Ethers are synthesized by the Williamson synthesis. This organic chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the williamson ether synthesis reaction mechanism.
The Williamson ether synthesis is the most widely used method to produce ethers. The Mechanism of Williamson Ether Synthesis.

Reaction Of Alcohols With Pbr3 Via Sn2 Mechanism Chemistry Organic Chemistry Chemistry Jokes

Some Reactions Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Reactions Organic Chemistry Mechanisms

Michael Reaction Michael Addition And Regioselectivity Of 1 2 Vs 1 4 Addition Organicchemistry Ochem Organic Chemistry Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Lessons

The Mechanism Of Grignard Reaction With Aldehydes Organic Chemistry Books Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study
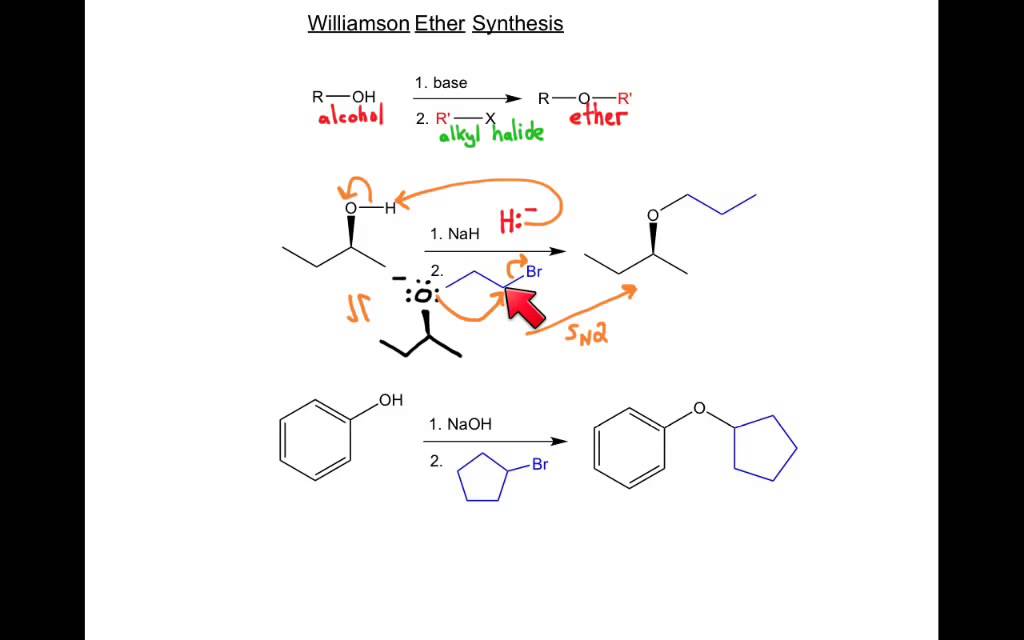
Williamson Ether Synthesis Basic Facts Ethereal Organic Chemistry

Complete Collection Organic Chemistry Chemistry Notes Teaching Chemistry

Wittig Reaction Examples Wittig Reaction Chemistry Chemistry Lessons

Anhydride Reduction Mechanism By Lialh4 Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Organic Chemistry Reactions

The Mechanism Of Organolithium Reaction With Nitriles Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Lessons

Imines And Enamines From Reactionaldehydes And Ketones With Amines Chemistry Biochemistry Notes Chemistry Lecture




Post a Comment for "Williamson Ether Synthesis Mechanism"